For many of us, thinking of how to improve gut health can seem like a daunting task. After all, it’s not something we often give much thought to. But the truth is, our gut plays an essential role in our overall wellness and vitality—so ensuring its optimal functioning is quite important.
Fortunately, there are some simple yet effective ways to naturally improve your gut health. Here are five tips to get you started:
The role of soluble and insoluble fiber
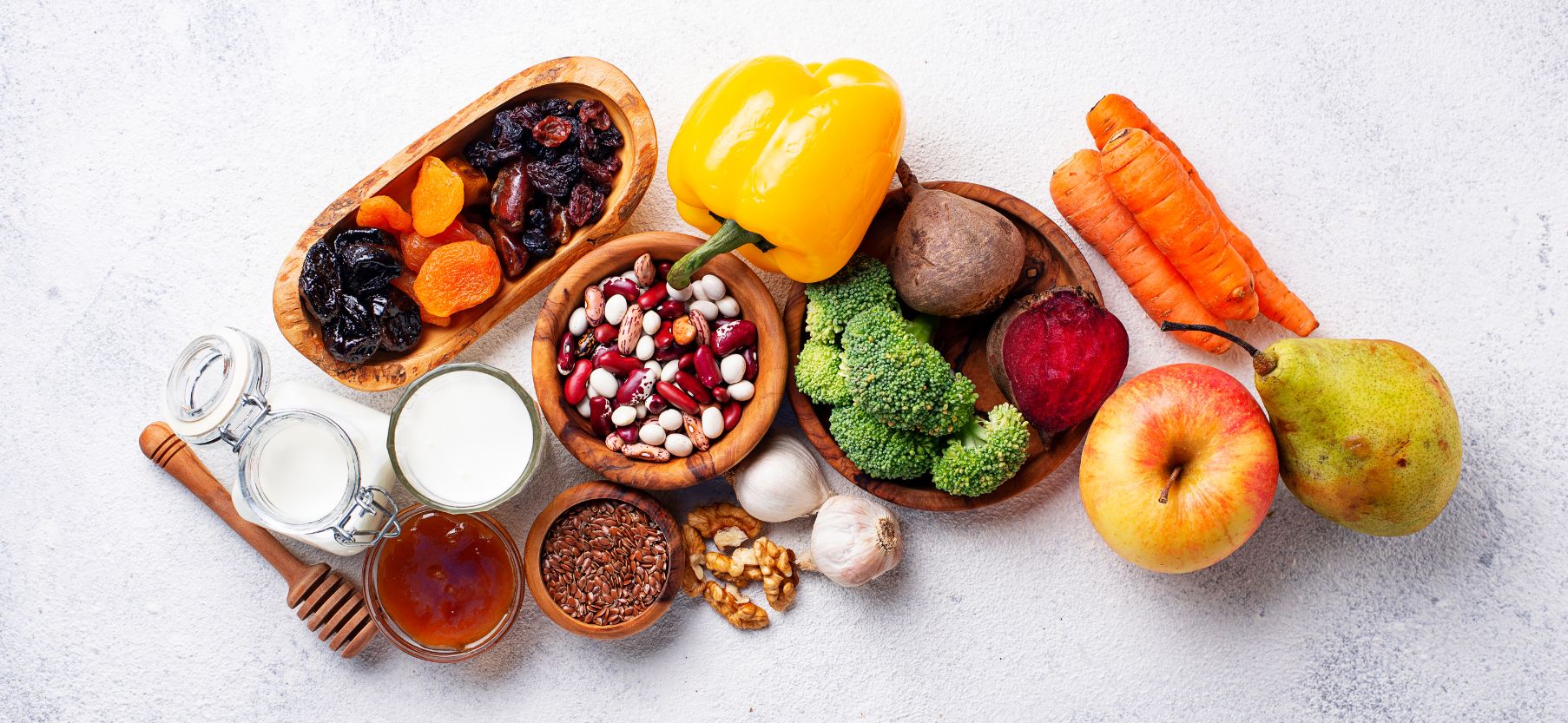
Fiber is important for gut health. There are two types of fiber – soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber helps keep you full by absorbing water and turning into a gel-like substance in your gut. Insoluble fiber does not absorb water, so it passes through the digestive system quickly and helps to keep things moving along smoothly.
Fiber plays an important role in promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, or probiotics, in the digestive system. It acts as a prebiotic, providing a food source for the probiotics to thrive. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds. Eating a diet rich in these foods can help to improve gut health and restore the balance of beneficial bacteria. Additionally, avoiding processed and refined foods that lack fiber can help to keep your gut healthy.
Probiotics vs. prebiotics
Probiotics are special types of bacteria that help keep your body healthy. Prebiotics are foods that help feed the probiotic bacteria in your large intestine. Probiotic-rich foods contain good bacteria that help to restore balance to the microbiome by crowding out bad bacteria. This helps your digestive system work better so you feel better.
Adding probiotic foods to your diet can help balance the microbiome and improve gut health. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, kombucha and kefir contain beneficial bacteria that restore good bacteria in the digestive system, improving digestion and promoting overall wellbeing. A 2021 study by researchers at Stanford University found that people who consumed a diet rich in fermented foods had not only increased microbiome diversity but reduced inflammation throughout the entire body.
Prebiotics are dietary substances that, when consumed by humans, act as a food source for beneficial gut bacteria. The most common type of prebiotic is soluble fiber, which helps to feed the beneficial bacteria found in the large intestine. Other types of prebiotics can include certain types of starches and sugars. Prebiotics have many health benefits, including improved digestive health and reduced inflammation in the gut.
How stress affects the gut
Stress can have a significant impact on our gut health and digestion, leading to a range of digestive issues. When we’re stressed, the body releases hormones like cortisol that disrupt our natural processes and put us in ‘fight or flight’ mode. This causes an increase in stomach acid production which can lead to heartburn, GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), indigestion and nausea. Stress also decreases blood flow to the digestive organs, resulting in slower digestion and constipation. Finally, stress has been associated with increased rates of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) due to its ability to alter how the brain interacts with the gastrointestinal system. In short, it is important for us to reduce stress levels if we want optimal gut health and digestion!

Managing stress is, of course, easier said than done. Meditation, breathwork, yoga, and time in nature are all well-known stress relieving practices, and if you’re looking for an extra hand, incorporating adaptogens like ashwagandha into your routine has also been shown to be beneficial.
Hydration and gut health
Hydration is essential for overall health and wellbeing, but it’s especially important when it comes to gut health. Proper hydration helps keep the digestive system functioning optimally by promoting regularity and allowing fiber to move easily through the intestines. It also helps the body to flush out toxins that can build up in the gut, which can lead to inflammation and a host of other digestive issues.

Additionally, staying well-hydrated may help reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on our digestion as well. The exact connection between hydration isn’t known, but some researchers hypothesize that it’s related to cortisol production, as increased cortisol production causes the body to lose more water through increased urination.

